Balancing and Alignment in Rotor Repair: Why Precision Matters for Turbine Efficiency
Gas turbine performance depends on the smooth and stable rotation of the rotor. Even small imbalances or misalignment can create vibration that reduces efficiency, accelerates wear, and increases the risk of mechanical failure. In modern power plants and industrial turbine applications, precision is not optional. It is a fundamental requirement for safe and reliable operation. This is why rotor repair services place such a strong emphasis on advanced balancing, alignment, and measurement techniques. These processes ensure that the rotor spins exactly as intended, allowing the turbine to operate at peak efficiency with minimal mechanical stress.
The Role of Rotor Stability in Gas Turbine Operation
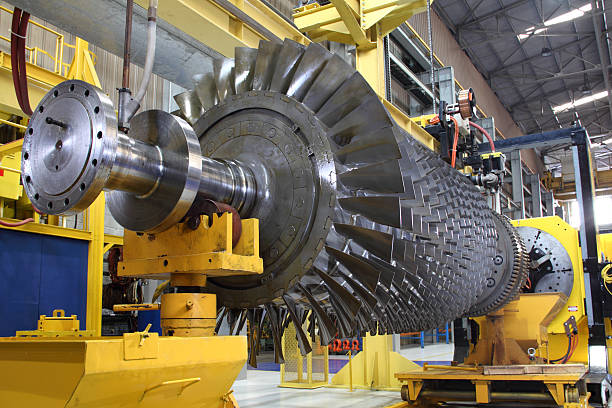
The rotor is the heart of a gas turbine. It supports rows of turbine blades and transfers mechanical energy from the hot gas path to the generator. At full speed, a turbine rotor can rotate at thousands of revolutions per minute. At these speeds, even a tiny mass imbalance or slight misalignment creates centrifugal forces that can quickly grow into damaging vibration.
Excessive vibration does more than create noise. It causes accelerated wear of bearings, seals, and couplings. It increases the risk of blade fatigue and crack growth. It also leads to efficiency losses because energy that should be converted into useful power is instead wasted in mechanical oscillations.
Rotor stability is therefore a direct driver of turbine efficiency, reliability, and service life. Precision balancing and alignment are the tools that make this stability possible.
What Causes Rotor Imbalance and Misalignment
Rotor imbalance occurs when mass is not evenly distributed around the centerline of rotation. This can be caused by many factors, including material loss due to erosion or corrosion, uneven repairs, manufacturing tolerances, or thermal distortion during operation.
Misalignment occurs when the rotor is not perfectly centered within its bearings or when individual rotor components are not aligned with each other. Stack misalignment can develop when rotors are assembled from multiple discs and spacers that are not optimally oriented.
Over time, these issues lead to higher vibration levels. Left uncorrected, vibration can cause a chain reaction of damage that spreads through the turbine.
The Importance of Dynamic Balancing
Dynamic balancing is one of the most important steps in rotor repair. It involves rotating the rotor at controlled speeds and measuring vibration levels to determine where mass imbalances exist. Using specialized sensors and software, technicians can identify both the location and magnitude of any imbalance.
Once the imbalance is known, corrective weights are added or small amounts of material are removed to bring the rotor back into balance. This process is repeated until vibration levels fall within strict acceptable limits.
Dynamic balancing ensures that the rotor spins smoothly at operating speed. It minimizes the forces transmitted to bearings and supports, reducing wear and extending component life. A well balanced rotor also produces more consistent power output and improves overall turbine efficiency.
Computerized Stack Optimization
Large gas turbine rotors are often built from multiple discs, spacers, and shafts stacked together. Each of these components has its own manufacturing tolerances and slight variations in mass distribution. When assembled randomly, these variations can add up to significant imbalance.
Computerized stack optimization is a powerful tool used during rotor assembly and repair. By measuring each component and using advanced software, technicians can calculate the best rotational orientation of each disc and spacer to minimize overall imbalance.
Instead of correcting imbalance only after the rotor is fully assembled, stack optimization addresses the problem at its source. By arranging components in their optimal positions, the rotor begins its life with far lower inherent imbalance. This reduces the amount of corrective balancing required later and results in a more stable and reliable assembly.
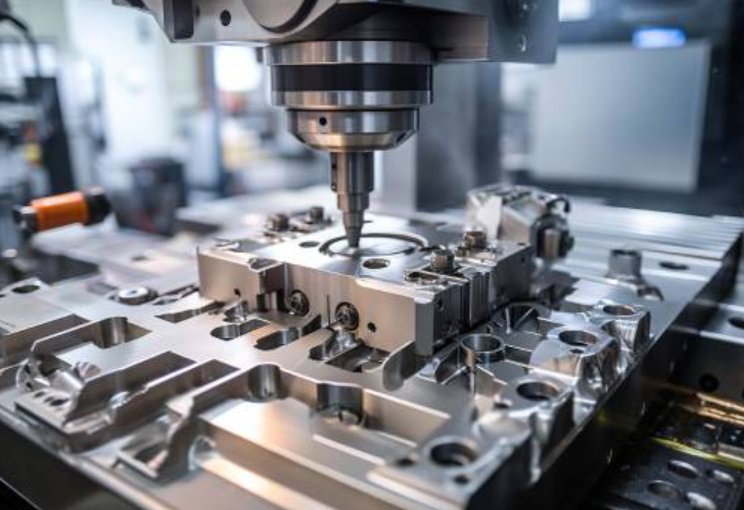
Tip Grinding and Its Role in Rotor Performance
Tip grinding is another critical process in rotor repair and optimization. Turbine blades have tips that run very close to stationary shrouds. This small clearance is necessary to maximize efficiency by minimizing the amount of gas that leaks around the blade tips instead of doing useful work.
Over time, blade tips can wear or become uneven due to erosion, rubbing, or thermal distortion. Uneven tips can cause both efficiency losses and vibration problems.
Tip grinding restores uniform blade height and profile across the rotor. By carefully removing small amounts of material, technicians ensure that all blades have the correct clearance and aerodynamic shape. This improves gas flow through the turbine and helps maintain balanced forces on the rotor.
Proper tip grinding also reduces the risk of blade rubbing, which can generate heat and further damage.
How These Processes Work Together
Dynamic balancing, stack optimization, and tip grinding are not isolated procedures. They work together as part of a comprehensive approach to rotor stability.
Stack optimization reduces the inherent imbalance of the assembled rotor. Tip grinding ensures that aerodynamic forces are evenly distributed across all blades. Dynamic balancing fine tunes the final assembly to eliminate any remaining vibration.
Together, these techniques create a rotor that is both mechanically and aerodynamically balanced. This balance is essential for smooth operation at high speed and high temperature.
See also: Transforming Sleep with Modern Technology
The Impact on Turbine Efficiency
A stable rotor is an efficient rotor. When vibration is minimized, more of the turbine’s energy is converted into useful work rather than being lost to mechanical motion. Bearings and seals operate under optimal conditions, reducing friction and leakage.
Even small improvements in efficiency can have a big financial impact over the life of a turbine. Reduced vibration also allows turbines to operate closer to their design limits without increased risk, enabling higher output and better fuel utilization.
Reliability and Equipment Protection
Precision balancing and alignment protect more than just the rotor. They safeguard the entire turbine system. Bearings last longer, seals maintain their integrity, and blade attachments experience lower stress.
This improved reliability translates into fewer forced outages and lower maintenance costs. Plants can plan maintenance more effectively and avoid the disruption of unexpected failures.
The Role of Advanced Measurement and Control
Modern rotor repair relies heavily on advanced measurement and control technologies. Laser alignment systems, high resolution vibration sensors, and powerful analysis software allow technicians to achieve levels of precision that were not possible in the past.
These tools ensure that every adjustment is based on accurate data. They also provide documentation that helps operators understand the condition of their rotors and track performance over time.
Conclusion
Balancing and alignment are at the core of effective rotor repair. Through dynamic balancing, computerized stack optimization, and precision tip grinding, technicians restore rotor stability and minimize vibration. This precision protects turbine components, improves efficiency, and supports long term reliability.
In a world where gas turbines must deliver more power with fewer interruptions, the accuracy of rotor repair services makes a measurable difference. By investing in precision, turbine operators ensure that their equipment continues to run smoothly, safely, and efficiently for years to come.